ML and AI in Manufacturing

Manufacturing is one of the main industries that uses Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to its fullest potential. Smart Factories, also known as Smart Factories 4.0, have major cuts in unexpected downtime and better design of products as well as improved efficiency and transition times, overall product quality, and worker safety. Artificial Intelligence is the heart of Industry 4.0, delivering more productivity while staying environmentally friendly.
Siemens, GE, Fanuc, Kuka, Bosch, Microsoft, and NVIDIA, among other industry giants are already heavily investing in manufacturing AI with Machine Learning approaches to boost every part of manufacturing. According to Google Trends, people were searching for “AI in Manufacturing” more than ever before.
Let’s start by explaining how exactly AI/ML in modern manufacturing can transform the industry.
How Can AI Help Manufacturing?
Smart Maintenance
Being a very important part of every asset-reliant production operation, maintenance of equipment is one of the biggest expenses in the manufacturing industry — unplanned downtime cost plants and factories nearly $50 billion, 42% of that was because of asset failure.
That’s why predictive maintenance became a vital solution that will help save an enormous amount of money. Complex AI algorithms like neural networks and Machine Learning are generating trustworthy predictions regarding the status of assets and machinery. The Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of equipment becomes significantly longer. If something needs to be repaired or replaced, technicians will know beforehand and even will know which methods to use to fix the issue.
Better Product Development
Generative design is the method that allows putting a detailed brief created by humans into an AI algorithm. The information in the brief can contain different parameters like available production resources, budget, and time. The algorithm examines all possible variations and generates a few optimal solutions. This set of solutions can be evaluated by pre-trained deep learning models, which can add more insights and pick certain options. You can go through this process as many times as you want to settle on the perfect one. Artificial Intelligence is completely objective without any unproven assumptions unlike humans can have.
Quality Improvement
In the modern world of short deadlines and the increased level of complexity of products, it becomes even harder to meet the highest standards and regulations in terms of quality. Customers expect impeccable products. Also, product defects can cause recalls, which massively damages the reputation of the company and its brand. AI can alert companies to problems in the production line that can result in quality issues. These faults could be major or subtle, but they all influence the overall level of production and could be eliminated in the early stages.
Machine vision, for example, is an AI solution that uses high-resolution cameras to monitor defects way better than a human can. It could be combined with a Cloud-based data processing framework that generates an automatic response. Also, manufacturers can obtain data on the performance of their products when they hit the market to make better strategic decisions in the future.
Market Adaptation
AI and ML are already an essential element of Factory 4.0, but they also can improve supply chains, making them interactive to changes on the market beforehand. Thus, managers can improve their strategic vision by relying on AI suggestions. Estimates are generated by AI based on linking together a number of factors such as political situations, weather, consumer behavior, and the status of the economy. Staff, inventory, and the supply of materials could be calculated according to predictions.
The biggest companies around the globe are already utilizing Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in manufacturing and investing millions in its development. Here are some of the most prominent examples of companies using it.
Siemens
The German conglomerate claims that its practical experience in industrial AI for manufacturing already boosted the development and application of the technology. For decades, they leveraged neural networks for monitoring steel factories as well as improving their performance. Over the last 10 years, they invested over $10 billion in the acquisition of software companies.
In 2016 Siemens presented Mindsphere, a smart Cloud that enables manufacturers to monitor machine fleets around the globe. They added IBM’s Watson Analytics to the functions offered by the service the same year. The purpose of this solution is to grab every parameter in the manufacturing process from development to delivery and find issues and the ways to solve them.

Siemens uses a neural network-based AI in their gas turbines. Over 500 sensors monitor various parameters, and the system learns and makes decisions on adjusting fuel values for the most efficient performance.
Siemens also offers Click2Make — a product that set a goal to make mass customization a reality. When companies have a complete understanding of their resources and have cutting-edge robots, it will be possible.
General Electric
One of the biggest companies on the planet, General Electric makes everything from home appliances to massive industrial machinery. They have over 500 plants worldwide, but they have only just begun to make them smart.
Brilliant Manufacturing Suite is an attempt from GE to track and process everything in every aspect of manufacturing to find all possible problems and failures. Their first Brilliant Factory in India received $200 million in investments and raised the effectiveness rate of the facility by 18%, thanks to this solution. GE’s Brilliant Manufacturing Suite aims to connect all elements of manufacturing, such as design, engineering, or distribution, into one global smart system that is scalable. It even has its own Industrial IoT platform Predix. This platform uses sensors to monitor all aspects of the manufacturing process and the performance of sophisticated equipment. Predix has deep-learning capabilities that can process all that information and come up with actionable insights.

At the moment, General Electric runs seven Brilliant Factories with the Predix system; all have seen positive improvements in production.
Fanuc
This company from Japan implements AI to make robots smarter. In fact, it is a leader in industrial robotics by integrating deep learning into robots. Fanuc collaborated with Rockwell and Cisco to introduce the FANUC Intelligent Edge Link and Drive (FIELD), an IoT platform for the manufacturing industry. The partnership with NVIDIA resulted in using Fanuc’s AI chips for the factories of the future. The usage of deep reinforcement learning led to the ability of some industrial robots to train themselves. FANUC and NVIDIA aim to enable multiple robots to learn simultaneously. If robots can learn together, it will be faster for each of them individually. In the future, robots will be able to share their skills with each other — saving time in the manufacturing processes in the Smart Factory.
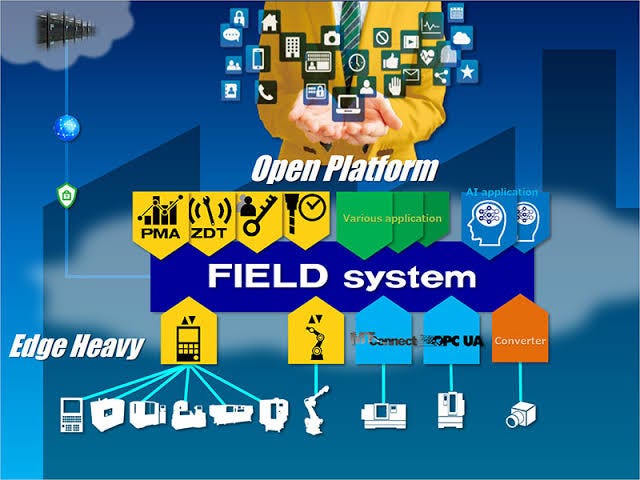
For years robotics, advanced analytics, and automation has been a major part of the manufacturing industry. The increasing scale of adoption of AI in manufacturing seems more like an evolution, rather than an industry disruption. Technology is already here and more massive implementation is a matter of time.
